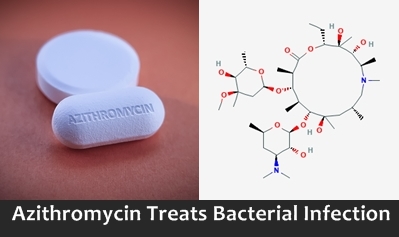
Chemical Formulae – C38H72N2O12
Weight – 748.9845 mg
Table of Contents
Bacterial Strain & Related Diseases Cured by Azithromycin
It is a broad-spectrum antibiotic effective on gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. In other words, it is a macrolide with bacteriostatic activities. One must take this medicine on a doctor’s advice. Otherwise, it may cause antibiotic drug resistance. Azithromycin can cure the following diseases:
- Skin infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae bacteria.
- Sinus infection caused by Moraxella catarrhalis and Streptococcus pneumonia, and
- Pneumonia acquired from community caused by S. pneumonia, Chlamydia pneumoniae, Mycoplasma, and Haemophilus influenzae. Azithromycin treats diplococcus gram negative bacteria causing pneumonia.
- COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) caused by S. pneumonia and M. catarrhalis.
- Tonsillitis caused by S. pyogenes.
- Cervicitis and urethritis caused by Chlamydia trachomatis.
- Chancroid genital ulcers caused by Haemophilus ducreyi.
- Ear infection in children caused by M. catarrhalis .
- AIDS caused by Toxoplasmosis.
- Gonorrhoea infection in throat and rectum. (2)
Also Read- 12th Nov – World Pneumonia Day
Mechanism of Action
The nature of bacteria is to replicate, and to do so, they undergo a specific process with the help of protein synthesis. These are ribosomal proteins.
Azithromycin initiates the ceasing activity by binding with the 23S rRNA of the 50S ribosomal subunit of the bacteria. To precisely stop the bacterial infection, it stops the protein synthesis process by inhibiting the assemblage of the 50S ribosomal subunit. Azithromycin is a macrolide that has a strong affinity for bacterial ribosomes.
This drug is highly stable in low pH that cast a long half-life to the serum by increasing the concentration in the tissues. (3)
Bio Absorption
37% of azithromycin is orally absorbed. It is generally absorbed in the intestine by the P-glycoprotein efflux transporter encoded by ABCB1 gene. Its half-life is 68 hours. It is not applicable for antibiotic resistant bacteria treatment. (4)
Dosage
The Azithromycin dose varies from 500mg to 2g based on the severity of bacterial intrusion. One may take it for a maximum of 5 days. In the case of urinary infection, one single dose of 2g can be taken.
Two modes of administration are tablets and suspension. While taking the liquid suspension, one must use a measuring cup, dosing spoon, or oral syringe. As the right dosage is very important to cure the ailment. (5)
Side Effects
- Headache
- Nausea
- Stomach pain
- Dizziness
- Rash
- Swelling of skin
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite (6)
Quality API to Prohibit Drug Resistance
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients is the medicinal part of a medicine. Therefore, its quality makes a great difference. The matter of antibiotic resistance is a point of global awareness. Anzen Exports makes sure to export the best quality API across the globe. For the last 30 years, it is serving mankind in combating diseases. Our success is directly proportional to the success of our clients. Therefore, we are dedicated to sourcing standard API, exporting those to clients on time, and providing exclusive after-sales service.
To know more about our product line related to API, Herbal extracts, and Nutraceutical extracts, connect with us. Read our blogs on updated topics of the medical industry and variant functions of different medicines. Share your experience and comments with us in the comment section.
Disclaimer:
Anzen Exports’ blog posts are based just on our research from cited websites. To be best informed, we advise consulting a doctor about an ingredient or medicine prior to taking it.
Sources:
- Medical News Today
Website – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/325721#what-does-it-treat - WebMD
Website – https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-1527-3223/azithromycin-oral/azithromycin-250-500-mg-oral/details/list-conditions - Drug Bank
Website – https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00207 - Drug Bank
Website – https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00207 - Medline Plus
Website – https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a697037.html - PubMed
Website – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1280567/
