World Health Organization (WHO) classifies essential nutrients into two categories; macronutrient and micronutrients. These nutrients play a pivotal role in maintaining a healthy lifecycle and protection from diseases. The body cannot produce the nutrients; hence, it has to be derived from a dietary source. A balanced diet refers to the consumption of an equitable amount of nutrients in diet that is required by an individual based on their age, height, and profession. Any disequilibrium results in malnutrition or obesity. Both excess and less intake can lead to syndromes. Besides proper food, the right intake of water is also very important, as it intoxicates the body and benefits health in numerous ways. (1)
Table of Contents
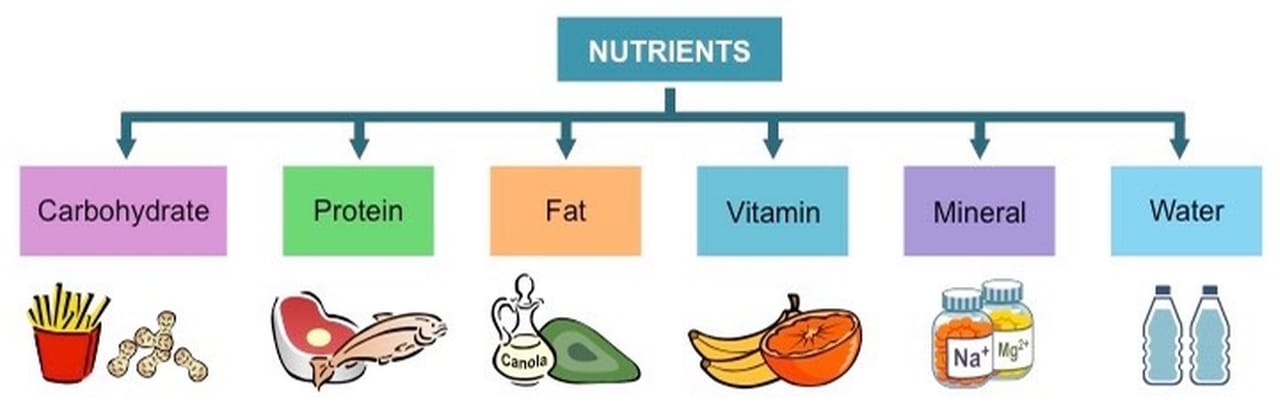
Constituents of Macro & Micronutrients
To understand, which nutrition for your diet is necessary, let us subcategorize macro and micronutrients. Macronutrients are: (2)
- Carbohydrate
- Protein
- Fat
- Water
Micronutrients are:
- Vitamins
- Minerals
Different components of Minerals:
Carbohydrate
Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends that a person should take 45-65% of the daily required calorie from carbohydrate. It is one of the most important nutrients in food that comes in form of starch or sugar, which provides vitality to cells and tissues of the body. It can be subdivided into simple and complex carbohydrates. A complex carbohydrate is preferable over simple carbohydrates, which are as follows:
- Brown rice
- Whole grains
- Oatmeal
- Barley
- Fruits
Protein
Proteins have a vast nutrients benefits; it is a building block of the human body cells. It ensures the growth and development of the muscular-skeletal system, cells, tissues, hair, and skin. It also helps in forming hormones, antibodies, and other essential mechanisms in strengthening the immune system.
Animal protein is a major source. There are many vegetarian products rich in protein as well. Some major sources of protein are:
- Egg
- Fish
- Mutton, chicken, turkey
- Dairy products
- Soy
- Nuts
- Legumes
- Pulses
Fat
Fat, unlike what most people think, doesn’t mean unhealthy for the body. Fat helps maintain optimal health. When asked “What to eat for a diet?”, dieticians and nutritionists often include food that contain unsaturated fat in the diet chart. There are two categories of fat:
- Saturated – Due to no double bond in chemical structure they get saturated or condensed at room temperature. Consuming this type of fat may induce the risk of cardiovascular diseases, cholesterol, and other obesity related ailments. Mutton, pork, full-fat dairy products, coconut oil, palm oil, etc.
- Unsaturated – It has a proportion of fatty acid molecules that has one double bond and fewer atoms of hydrogen than carbon chains. It is generally present in plant based foods, seeds of fruits, and some fishes like salmon and tuna. (3)
Functions of fat are as follows:
- Brain functioning
- Absorption of minerals and vitamins
- Muscular movements
- Balancing insulin level in the blood
- Production of hormone
- Making of new cells
Vitamin
The benefits of vitamins are numerous. There are 13 essential vitamins required for the human body, which can be classified into two categories; fat soluble and water soluble vitamins. Any diet enriched with vegetables, proteins, and fruits can accomplish the vitamin requirement of the body. It helps to:
- Strengthen the immune system
- Reduce the risk of malignancy
- Metabolize proteins, carbohydrates and absorbs calcium
- Support the functioning of the nervous system.
Fiber
Dietary fiber helps to reduce body weight and maintain a healthy gut system. It reduces the risk of constipation, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and some variations of cancer as well. Rich sources are leafy vegetables, fruits with their peel, nuts, oats, etc.
Potassium
It regulates muscle contractions and relaxation, nerve signals, and balances fluid. It prevents osteoporosis, high blood pressure, kidney stones, and water retention. Enriched food sources are: (4)
- Banana
- Apricot
- Orange
- Potatoes
Calcium
Calcium is majorly required by the body to maintain the health of the bones. Furthermore, muscles, teeth, nail, and hairalso need calcium to maintain sturdiness. One of its major functions is to support nerves to carry stimulus to the brain. Its predominant source is dairy products. Fish, grains, and some vegetables are some potent sources too. (5)
Iron
Iron executes the metabolic process of the body like transport of oxygen, deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis (DNA), electron transport, prevents anemia, and neurodegenerative diseases. Sources are: (6)
- Cereals
- Pulses
- Legumes
- Fruits
- Vegetables
Zinc
The body requires zinc to make DNA and other genetic materials in cells. It also helps the immune system to fight intruding viruses and bacteria. Sources: (7)
- Oysters
- Seafood
- Whole grains
- Dairy products
Magnesium
Magnesium makes more than 300 enzymatic reactions in the body. It regulates functions related to muscles, nerves, bones, cardiovascular system, premenstrual symptoms, and immune system. Sources are:
- Potato
- Almond
- Soy
- Whole wheat
- Cashew
- Spinach
- Banana
- Cereals
Supplements to Support Deficiency
Essential nutrients are not synthesized by the body; therefore, it needs to be derived from the food. In case it cannot be obtained from the diet, then supplements are required to be taken. The dietary supplement market is a vast one and demonstrating outcome.
Anzen Exports is one of the leading herbal & nutraceutical extract exporters across the globe. It procures herbal extracts from Indian manufacturers and produces them for domestic and international herbal products manufacturers. Connect today with the sales team for more information.
Disclaimer:
Anzen Exports’ blog posts are based just on our research from cited websites. To be best informed, we advise consulting a doctor about an ingredient or medicine prior to taking it.
Sources:
- BBC
Website – https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zyjx6sg/revision/1
- Medical News Today
Website – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/326132#carbohydrates
- La Tourangelle
Website – https://latourangelle.com/general/differences-between-saturated-and-unsaturated-fats/
- Health Harvard
- National Institute of Health
Website – https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Calcium-Consumer/
- NCBI
Website – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3999603/
- National Institute of Health
Website – https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Zinc-Consumer/
- Medical News Today
Website – https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/286839#_noHeaderPrefixedContent
