
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common type of arthritis, usually characterized by gradual wear and tear and a loss of the cartilage in the joints resulting in friction between the bones. It may lead to swelling in the local area along with pain.
In OA, the periarticular bone reacts with the osteophyte formation, causing increased restriction in the movement of the joint. It predominantly occurs in weight-bearing joints such as the knee and hip joint. Total joint replacement is a popular remedy, but drugs such as Glucosamine Sulfate are also effective. (1)
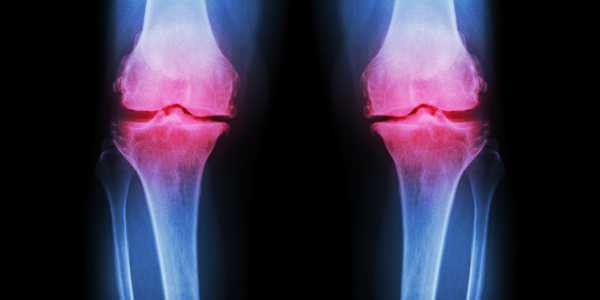
Table of Contents
Glucosamine Sulfate: Cartilage Repair
The synovial fluid is viscous and composed mainly of hyaluronic acid, lubricin, glucose and water. Hyaluronan is synthesized by the synovial membrane and released into the joint cavity. So, it is seen that Glucosamine, hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate are essential natural components of the cartilage and synovial fluid. In OA, there is a disturbed balance between the catabolic and anabolic processes. Thus supplementation of these natural components becomes essential.
Glucosamine is an amino monosaccharide synthesized from glucose in the tissue. It is especially abundant in the connective tissue and cartilage. It can be extracted from chitin, found in the exoskeleton of the crustacea as prawns and crabs and the mushrooms’ cell membranes.
It is necessary for forming hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate, and keratan sulfate, which are essential components of the synovial fluid and the articular cartilage. So, its role in treating cartilage repair and regeneration is critical.

Role in Medicine
Glucosamine sulfate is a naturally occurring chemical found in the human body. It is oral drug therapy for osteoarthritis, glaucoma, weight loss, joint pain caused by drugs, a bladder condition called interstitial cystitis, jaw pain, joint pain including knee pain, back pain, multiple sclerosis, and HIV/AIDS. Glucosamine is sometimes even used in skin creams to control arthritis pain. These creams contain camphor and other ingredients as well.
Glucosamine sulfate is used parenterally for osteoarthritis. It is used by the body to produce other chemicals used to build tendons, cartilage, ligaments, and the thick fluids surrounding joints. In OA, this cartilage breaks down and becomes thin. Glucosamine supplements may either increase the cartilage and surrounding fluid joints or help prevent the breakdown of these substances, or maybe both. The sulfate part of the Glucosamine Sulfate is also essential, as Sulfate is needed to produce cartilage. So, the effect it has in the treatment of OA is considered primary.
Glucosamine Sulfate can provide some relief for patients with OA, especially of the knees. Apart from relieving pain, glucosamine sulfate might also slow the breakdown of joints and prevent the condition from getting worse if taken for several years. Evidence shows that people who take glucosamine sulfate might be less likely to need total knee replacement surgery.
Side Effects
Some common mild side effects observed in Glucosamine Sulfate administration may be nausea, heartburn, diarrhoea, and constipation. Side effects, usually rare, are drowsiness, skin reactions, and headaches. In pregnancy, lactation, asthma, diabetes, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, allergy to shellfish and during surgery periods, the administration of Glucosamine should be avoided.
When taken orally, the optimal dosage for Glucosamine Sulfate for osteoarthritis is 1500 mg once daily or 500 mg three times daily, either alone or together with 400 mg of chondroitin sulfate twice or three times daily for up to 3 years. For skin application, a cream containing 30 mg/gram of glucosamine sulfate, 50 mg/gram of chondroitin sulfate, 140 mg/gram of chondroitin sulfate, 32 mg/gram of camphor, and 9 mg/gram of peppermint oil has been applied to the skin as needed for eight weeks. As injections, the optimal dosage is: 400 mg of glucosamine sulfate has been injected twice weekly for six weeks.
Besides the typical OA therapy with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), the treatment with chondroprotective, such as glucosamine sulfate, is a promising therapeutic approach.
Anzen Exports: Prominent in Healthcare
Anzen Exports is renowned for manufacturing and exporting high-quality Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, herbal extracts, nutraceutical ingredients, and cosmetic ingredients. Anzen was involved in domestic trading and export of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. The company used the best of its resources and workforce to strengthen its network with the finest manufacturers in India.
Anzen Exports is vertically integrated into the healthcare industry. It works towards the common goal of providing the best services for the needs of the Pharmaceutical Industry.
For more details, visit www.anzen.co.in
Disclaimer:
Anzen Export’s blog posts have been written with the information gathered from approved medical journals and websites online. Our research and technical team strive to provide relevant information through such articles. We advise consulting a doctor about an ingredient or medicine before taking it to be best informed.
References:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3150191/
- https://www.rxlist.com/glucosamine_sulfate/supplements.htm
