Methocarbamol: A good muscle relaxant for neck and back pain
Methocarbamol is the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) present in generic and branded muscle relaxant medicines. Muscle relaxants are useful for treating acute pain from muscle spasms, which are involuntary muscle contractions. Typical uses of methocarbamol include lower back spasms, neck pain, and arthritis pain.
Muscle relaxants are medications that help reduce acute pain associated with musculoskeletal conditions. If your pain is from a spine-related problem, such as low back spasm, whiplash or fibromyalgia, and it limits your mobility, you need medical attention (SpineUniverse).
What are musculoskeletal conditions?
Did you know that there are over 150 different musculoskeletal disorders? (Healthline)
The most common causes of musculoskeletal pain is injury to the bones, muscles, joints, ligaments and tendons. They are usually short term but can sometimes last a long time. For example, if you suddenly fall, lift something heavy, have a sports injury, while working out, or get injured in a car accident, it may lead to chronic pain.
Whether you have a new injury or an inflamed old one, muscle stiffness and soreness in the neck and back can give you sleepless nights. Muscle relaxants work best if you use them at night. They help alleviate acute neck and back pain (GoodRx)
How does methocarbamol work?
Methocarbamol is a central nervous system depressant and muscle relaxant. Experts are not sure how methocarbamol works since the drug has no direct effect on muscle. However, it has sedative properties, and relieves muscle pain by blocking nerve impulses to the brain (Drugs.com).
Most doctors recommend a muscle relaxant to reduce your back pain or neck pain to help your muscles move better. Nevertheless, it is not the sole treatment for a full recovery. Sometimes muscle relaxants, like methocarbamol are more effective used in combination with an OTC pain treatment (NSAIDs). Your mobility will also improve with rest, physiotherapy, and stretching exercises (SpineUniverse).
What are the finished forms?
The finished dosage of methocarbamol is available in both the solid (tablets/capsules) and liquid form (injection). For example, the generic brand name medicine, Robaxin 500 are round-shaped and light orange tablets packaged in a bottle.
Its chemical formula is C11H15NO5 and molecular weight is 241.24. This is what methocarbamol looks like at the molecular level (RxList):
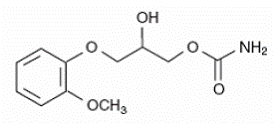
Molecular Structure of Methocarbamol
1. What is the dosage* of methocarbamol and response?
Usually, doctors prescribe muscle relaxants for short-term acute back or neck pain relief. Sometimes they are habit-forming, which is why doctors typically recommend taking the tablets for less than 2 weeks to reduce the risk of drug dependency (SpineUniverse).
Methocarbamol starts working after 30 minutes, and it is fully effective within 2 hours. This drug is relatively short-lived, so you may need to take it three to four times a day as directed by a physician.
Adults:
Methocarbamol is available in 500mg and 750mg tablets. For adults with muscle stiffness, the initial dosage is 1,500 mg, four times daily (Healthline):
OR
2 tablets (750 mg) 4 times per day
Recommended maintenance dosage (MedIndia):
*Dosage varies from person to person. Consult a doctor and use the prescribed dose for you.
Seniors:
- May increase the risk of falls, putting seniors are at higher risk.
Children and pregnant women:
- Safety for children below 16 years is yet to be determined.
- Women should avoid methocarbamol use during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
2. What tips for using methocarbamol should you follow? (Drugs.com)
- Take the prescribed tablet with or without food.
- Avoid drinking alcohol and alcoholic beverages while taking this medicine.
- Avoid driving or operating heavy machinery.
- You may feel dizzy while standing and are more likely to fall over, so avoid trip hazards.
- Use only if over the counter pain medication has not worked.
- Should not be used by children, seniors and women who are breastfeeding
- Check with your doctor before adding other medicines, including OTC.
3. Are there any methocarbamol side effects? (Drugs.com)
Drowsiness and dizziness are the most common side effects associated with muscle relaxants. Therefore, avoid doing tasks that require your full attention. Additionally, doctors do not recommend muscle relaxants if you have certain medical conditions, such as a liver or kidney problem, heart disease, diabetes, or seizures. These health problems will increase your risk of having side effects. Furthermore, using muscle relaxants containing the API, methocarbamol may result in side effects caused by drug interactions. Listed below are 10 common side effects of oral methocarbamol (Healthline):
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Low blood pressure
- Light-headedness
- Blurred vision
- Headache
- Fever
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Confusion
Tell your doctor if you see any of these serious side effects:
- Fever or chills
- Flu-like symptoms
- Slow heart rate
- Extreme dizziness
- Seizures (convulsions)
- Yellowing of your skin or eyes (jaundice)
Read the full side effects of Methocarbamol here.
4. Is it a narcotic?
Methocarbamol is not a narcotic. Sometimes it is mistaken to be one due to side effects like drowsiness and dizziness, which may feel like a drug “high” (Healthline).
5. What drugs interact with methocarbamol? (Drugs.com)
Methocarbamol is a CNS depressant, and this is why most drug warnings are about combining it with alcohol, similar depressants, or psychotropic drugs. Additionally, some medications and supplements, including sleeping pills, opioids, and St. John’s Wort increase health risks by interacting with muscle relaxants. Here are 10 common drug classes that affect methocarbamol:
- Anti-anxiety medications
- Anticonvulsants
- Antidepressants
- Antihistamines that cause sedation
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors
- Opioid analgesics
- Other muscle relaxants
- Sleeping pills
- Certain chemotherapy
- Mental illness medication
Note:
- Avoid excess dosage.
- Avoid alcohol consumption.
- To get the complete list, check your prescription information.
- Speak to your doctor about how to manage your drug interactions.
What do studies say?
Recent studies (Emrich et al.) revealed when methocarbamol used for 8 days, 44% of the people that took the muscle relaxant medicine had complete pain relief, compared to 18% who did not take anything. Additionally, there were not any serious side effects. It is also an inexpensive drug for treating acute neck and back pain. Furthermore, methocarbamol has a less sedative side effect (GoodRx) compared to other muscle relaxant API, like cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) and carisoprodol (Soma).
Another recent research (Patel et al.) shows that if a muscle relaxant is used with acetaminophen (NSAIDs), it improves musculoskeletal pain better than either medicine does alone.
What do patients say?
Read customer comments and online user reviews of methocarbamol use for back pain here.
Take home message
When you feel your first back or neck pain, your first line of treatment will still be over-the-counter painkillers like Tylenol or Ibuprofen. If the pain does not respond with OTC medications, then muscle relaxants containing the API, methocarbamol may be a good option for alleviating muscle spasms. Some people find it useful to combine one NSAID with methocarbamol, especially to sleep well at night. Either way, your methocarbamol treatment should be accompanied by gentle stretching, physiotherapy, and exercise, instead of being the only treatment for your back and neck pain.
To know more about or buy methocarbamol and other APIs from a reliable bulk drugs exporter in India, contact Anzen Exports.
Disclaimer:
Anzen Exports’ blog posts are based just on our research from cited websites. To be best informed, we advise consulting a doctor about an ingredient or medicine prior to taking it.
References:
Emrich OM, et al. “Methocarbamol in Acute Low Back Pain. A Randomized Double-blind Controlled Study.” PubMed Central (PMC) – NCBI, 13 July 2015, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26168743.
Highsmith, Jason M. “Muscle Relaxants for Back Pain and Neck Pain.” SpineUniverse, 5 Oct. 2019, www.spineuniverse.com/treatments/medication/muscle-relaxants-back-pain-neck-pain.
“Methocarbamol Drug Information – Indications, Dosage, Side Effects and Precautions.” Medindia, www.medindia.net/doctors/drug_information/methocarbamol.html.
“Methocarbamol Reviews & Ratings.” Drugs.com, www.drugs.com/comments/methocarbamol.
“Methocarbamol Side Effects.” Drugs.com, 7 Feb. 2019, www.drugs.com/sfx/methocarbamol-side-effects.html.
“Methocarbamol: 7 Things You Should Know.” Drugs.com, 6 Nov. 2019, www.drugs.com/tips/methocarbamol-patient-tips.
Orrange, Sharon. “Which Muscle Relaxants Are Best for Neck and Back Pain?” GoodRx, 21 Jan. 2020, www.goodrx.com/blog/best-muscle-relaxants-over-the-counter-prescription-medications/.
Patel, Himanshu D., et al. “Efficacy and Safety of Combination of NSAIDs and Muscle Relaxants in the Management of Acute Low Back Pain.” PubMed Central (PMC) – NCBI, 16 Jan. 2019, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6513919/.
Vandergriendt, Carly. “Is Methocarbamol a Narcotic?” Healthline, 24 Aug. 2018, www.healthline.com/health/is-methocarbamol-a-narcotic.
Watson, Stephanie. “Musculoskeletal Pain: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment.” Healthline, 21 Oct. 2019, www.healthline.com/health/tgct/musculoskeletal-pain.

